Design Study on the Relationship between Problem Framing and Solution
- Ahmed Mohammed Sayed MOHAMMED / 九州大学大学院芸術工学府デザインストラテジー専攻
- Ahmed Mohammed Sayed MOHAMMED / Graduate School of Design, Kyushu University
- 平井康之 / 九州大学大学院芸術工学研究院
- HIRAI Yasuyuki/ Faculty of Design, Kyushu University
Keywords: Design Thinking, Problem Framing, Human Centered Design
- Abstract
- Understanding the relationship between problem framing and solutions helps designers to navigate their way of thinking to make sure that the final solution meets user's needs and desires.This research analyzes different case studies done by different organizations and design studios, Then proposes a criteria that structures how the relationship between problem framing and solutions works.The proposed structure is based on Kees Dorst framework of "Frame Innovation". By understanding this relationship, designers can create different themes for solving a design problem and they would be able to translate those themes into wide range of solutions.This research also pointed out main five points that draws this relationship which are "Problem Layers", "Problem Context", "Themes", "Solution Concept" and "Values".
目次
目的と背景 Research Goal and Background
The importance of framing in design relies not only in creating a new way of viewing a problematic situation, but it also creates particular outcome spaces that afford a different range of responses. That’s why framing is often considered as the creative step that allows for original solutions to be produced.[1] In his book, Dorst also pointed out that nowadays problems are “open, complex, dynamic, and networked” as the nature of the problems we face consists of many elements which change overtime and that makes the system borders unclear, so that makes us to change our conventional way of thinking.[2] The main goal of this research is to find criteria that structures the relationship between problem framing and solutions in design. As this research tries to show the importance of understanding this relationship,so designers can face complex design problems in a way that creates different range of solutions. The main challenge here is not only to develop criteria for complex problems ,but also to make sure that this criteria creates benefits for all stakeholders in the problem context.
研究の方法 Research Method
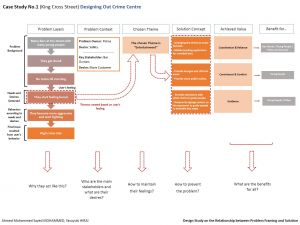
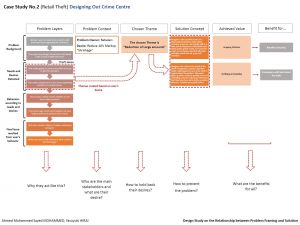
This research analyzes different case studies done by different organizations and design studios.Case studies were selected based on their fields to ensure variety of the final solutions to see how the relationship between problem framing and solutions work in different design fields. Around eight different case studies were collected from Designing Out Crime Center, IDEO and Digital Surgeons, then they were analyzed into details using relationship diagrams in a way to have a holistic view from the beginning of the design process till the final solution.This analysis is based on Dorst "Frame Innovation" framework that he proposed in his works.The proposed structure starts from the known part of the abduction equation as designers need to start from user's hidden needs and desires (Outcome) then they can think of objects or systems (What) with certain working principles (How) to achieve desired values.[3]
結果 Results
This research proposes a criteria that structures how the relationship between problem framing and solutions works.The proposed structure is based on the understanding of five different points through the design process. These points are identified as following:
- Problem Layers:Through problem layers, users’ needs and desires can be detected and the main issue can be realized. problem layers are explored by understanding the problem background,user's needs and desires, user's behaviors and the main issue.
- Problem Context:In the problem context step,main stakeholders are identified and their desires and behavior are realized.
- Themes:Themes could be created based on user’s needs, desires and actions or based on the main issue that resulted from user’s behavior.
- Solution Concept:Solution concept is the answer of one of these two questions: How to prevent the problem and deal with it before it happens? Or How to deal with it after it happens?
- Achieved Values:Values are the ultimate goal of the design process. Achieved values should be relevant to all stakeholders in the problem context.
After framing the design problem, the next step is to create themes which are the start of creating solutions.Through the analysis of case studies, created themes found to be based on either user's desires or based on the main issues. In the case of user's desires, solutions will be oriented to how to deal with the problem before it happens, but in the case of the main issue, solutions will be oriented to how to deal with the problem after it happens. This way of approaching design problems creates wide range of solutions and possibilities.
考察 Discussion
If we have a look at the resulted solutions in each of the previous examples, we will find out that these solutions need to be criticized regarding their cost and sustainability as many of these solutions could be creative, but they cost more than others or they are one time solutions not sustainable ones, so a parameter needs to be created to measure the credibility of each of these solutions compared to the achieved value and the resulted benefit on user's and stakeholders. Another point that needs to be discussed is that this holistic map focuses at the beginning on understanding user's need and desires and how they act like that.These needs and desires need to be realized in many levels as what users desire is derived from what they say, do, act or feel.In some recent design fields, we can notice that designers start designing based on their own aspiration.In that case designers create the need rather than looking for it, which is another level of design.
まとめ Conclusion
Recently design thinking became more popular between many organizations and startups because of its ability to solve problems in more creative ways. Recent researches focus on the advantages of design thinking and its ability to tackle more complicated problems,but this research tries to visualize a structure to help designers and researchers understand how design thinking works and how the relationship between problem framing and solutions could be structured with objective criteria. In future research this proposed structure needs to be tested with some real life problems to see the credibility of it.
脚注 References
- ↑ Bec Paton, Kees Dorst, "Briefing and re-framing: A situated Practice," Design Studies, vol. 32, pp. 573-587, 2011.
- ↑ K. Dorst, Frame Innovation: Create New Thinking by Design, London: The MIT Press, 2015.
- ↑ K. Dorst, "Frame Creation and Design in the Expanded Field," The Journal of Design, Economics, and Innovation, no. 1, pp. 22-33, 2015.
参考文献・参考サイト Website References
- http://designingoutcrime.com/project/petrol-theft/ (2019年11月3日 閲覧)
- http://designingoutcrime.com/project/opera-house/ (2019年11月3日 閲覧)
- https://www.ideo.com/case-study/designing-the-future-kitchen (2019年11月3日 閲覧)
- https://www.ideo.com/case-study/designing-waste-out-of-the-food-system (2019年11月3日 閲覧)
- https://www.digitalsurgeons.com/case-studies/district-new-haven/ (2019年11月3日 閲覧)
- https://www.digitalsurgeons.com/case-studies/imend/ (2019年11月3日 閲覧)